
Relay Attack: Concept, a use case, and countermeasures
Concept of the relay attack
In the world of cybersecurity, the relay attack is a hacking technique that can be used for keyless car theft or making unauthorized contactless card payments. The relay attack is similar to the man-in-the-middle (MITM) and the replay attacks, but there are some subtle differences. In the MITM attack, an attacker intercepts the data sent from the sender, views and modifies it, and then send the altered data to the original or another recipient. In the replay attack, an attacker steals and saves the contents of an authentication message and sends the unaltered message to the recipient. Later the attacker uses the saved message (replay) to access a server to initiate a new session. Note that both in MITM and replay attack, the sender and receiver have initiated the communication. In a relay attack, an attacker intercepts the communication between two parties and relays the signal unaltered to another device. Here neither the sender nor the receiver has initiated the communication.
How keyless car door unlocks
In many modern cars, the traditional key has been replaced by the “key fob” to facilitate the remote keyless entry system. A key fob uses radio waves (315 MHz) to communicate with a reader in the car door latch, which is programmed to open. Both the key fob and reader can send and receive encrypted RFID radio signals. When the key fob is close to the reader, typically within 5 to 20 meters,
the locking mechanism in the car door opens, and the person carrying the key fob gains access to the car.
Relay attack to open a keyless car door
In the following, with the help of Figure 1, we describe how the relay attack is used to unlock a keyless car door and steal it. The West Midlands Police in the UK has shared a YouTube video of keyless car theft by using the following steps sequentially:
- 1. Attacker 1 sends a signal to the reader in car door by using a fake key fob device.
- 2. An authentication request is sent from the car reader.
- 3. The authentication signal is sent to the attacker 2, who is near the home looking for the signal from the original key fob.
- 4. Attacker 2 relays the signal to the key fob inside the home.
- 5. The key fob transmits the credentials.
- 6. Attacker 2 relays the credentials back to attacker 1, who uses this credential to unlock the car door.
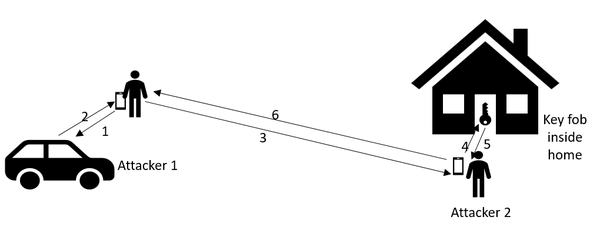
Figure 1: Car theft using relay attack
Protective measures
To avoid car theft by the relay attack, one should adopt several protection measures:
- Avoid placing the key fob near the home entrance or window. It is better to keep the key fob inside an RFID protective case so that attacker 2 in Figure 1 cannot listen to it.
-
Keep fobs software updates. If possible, use the sleep mode with the key fob.
-
Use a steering lock and a secured car garage.