ExpressVPN is leveling up its gaming presence with major new esports partnerships across Riot Games, G2 Esports, and Method, and promises exclusive drops, faster speeds, and stronger security for players.
<ul><li>ExpressVPN renewed its League of Legends EMEA Championship (LEC) deal</li><li>The VPN also signed new partnerships with VCT, G2 Esports, and Method</li><li>Fans can expect rare in-game loot, … [+3989 chars]
Adrian Grenier is making his way back to the big screen with a story built around one of the internet’s most intriguing mysteries: lost cryptocurrency. The Entourage star headlines the new thriller “Self Custody,” which is now streaming on Amazon Prime Video.…
Adrian Grenier is making his way back to the big screen with a story built around one of the internets most intriguing mysteries: lost cryptocurrency.
The Entourage star headlines the new thriller S… [+3967 chars]
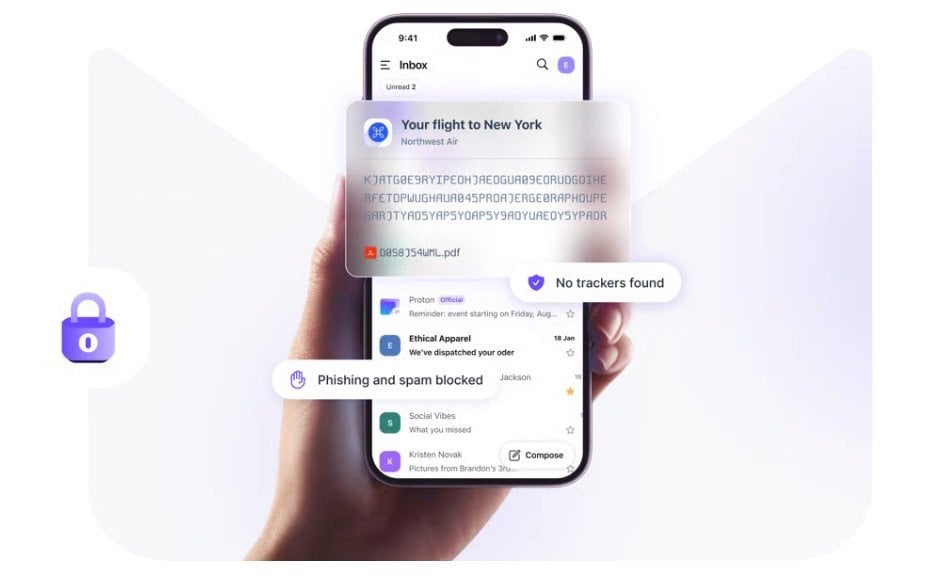
Proton Mail has become a cornerstone for privacy-conscious individuals in 2026, offering encrypted email services that prioritize user security. In a recent guide by CyberInsider, the focus is on how Proton’s ecosystem, spanning services like ProtonVPN, Proto…
Proton Mail has become a cornerstone for privacy-conscious individuals in 2026, offering encrypted email services that prioritize user security. In a recent guide by CyberInsider, the focus is on how… [+7576 chars]
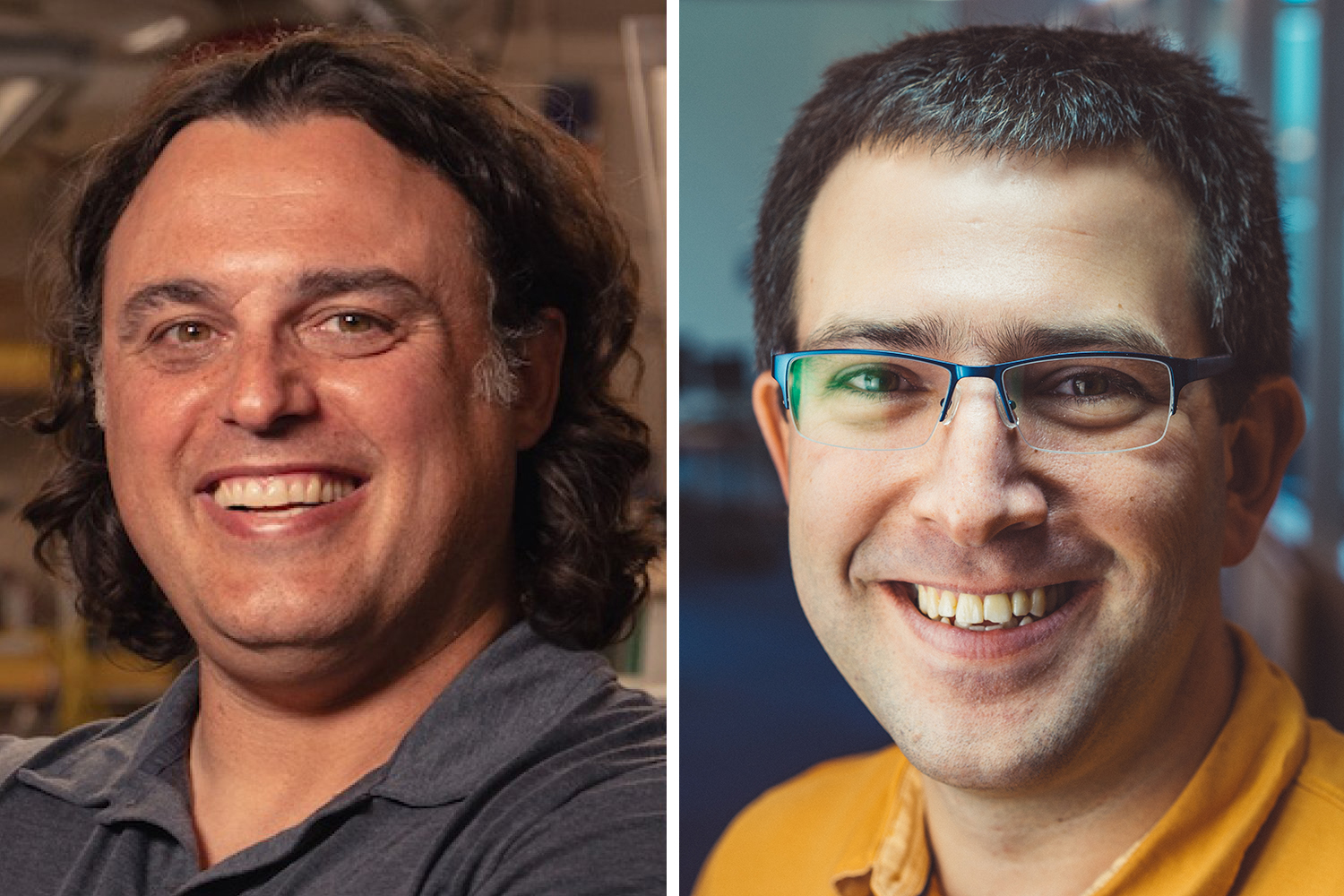
Two outstanding MIT educators were named 2026 MacVicar Faculty Fellows: Amos Winter, professor of mechanical engineering, and Nickolai Zeldovich, professor of electrical engineering and computer science.
Two outstanding MIT educators have been named MacVicar Faculty Fellows: professor of mechanical engineering Amos Winter and professor of electrical engineering and computer science Nickolai Zeldovich… [+8639 chars]
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) today issued two precedential decisions in The Trustees of Columbia University of the City of New York v. Gen Digital Inc., reversing, vacating and remanding a district court judgment that Columbia’s pa…
The claimed inventions efficiency gain from the use of multiple computers is no more than [the] concededly abstract idea. – CAFC
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) today issued… [+5815 chars]
Fortanix announced a new multi-sourced quantum entropy capability within Fortanix Data Security Manager (DSM), enabling enterprises to diversify encryption key generation at the origin of trust. Through partnerships with Qrypt and Quantum Dice, Fortanix integ…
Fortanix announced a new multi-sourced quantum entropy capability within Fortanix Data Security Manager (DSM), enabling enterprises to diversify encryption key generation at the origin of trust.
Th… [+4350 chars]
Data security company Fortanix Inc. today announced a new multi-sourced quantum entropy capability within Fortanix Data Security Manager that allows enterprises to diversify encryption key generation at the origin of trust. The update combines quantum randomn…
Data security company Fortanix Inc. today announced a new multi-sourced quantum entropy capability within Fortanix Data Security Manager that allows enterprises to diversify encryption key generation… [+4649 chars]
A demat account is a digital repository for holding equity shares and financial securities, eliminating the need for physical certificates. It works in conjunction with trading and bank accounts, enabling efficient and secure transactions. Essential for begin…
The stock market provides pathways to build long-term wealth. However, one must first learn investing basics before attempting to navigate this financial landscape. As a beginner, one might find the … [+8051 chars]
Regular maintenance of your iPhone is crucial for making sure it operates efficiently, remains secure, and protects your valuable data. By dedicating a few minutes each week to essential upkeep, you can extend your device’s lifespan, enhance its performance, …
Regular maintenance of your iPhone is crucial for making sure it operates efficiently, remains secure, and protects your valuable data. By dedicating a few minutes each week to essential upkeep, you … [+4600 chars]
Protect yourself against SIM swapping and more security threats by setting up a SIM PIN right now.
Your SIM card is far more important than you probably realize. It's not just the chip that is assigned to your phone number and contains crucial network authorization data. It can store contacts and … [+6098 chars]
Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ:MSFT) is one of the top stocks that will make you rich in 10 years. Reuters announced on March 5 that Microsoft Corporation...
Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ:MSFT) is one of the top stocks that will make you rich in 10 years.
Microsoft Corporation (MSFT) and Codelco Announce Signing of AI Deal for Mining Operations, Reuters … [+1950 chars]
The findings of the study come at a time when online anonymity is under threat, not just from AI models but also due to the spread of age-gating mechanisms.
Artificial intelligence (AI) helps unlock powerful new capabilities nearly every day, but its rapid progress continues to widen the scope for potential misuse. The latest addition to the list of AI-d… [+3618 chars]
TikTok Canada has reached a major agreement with the federal government that will keep its local operations and jobs in place. Since opening Canadian operations in 2020, the company has grown to a point where more than 16 million Canadians now use the platfor…
TikTok Canada has reached a major agreement with the federal government that will keep its local operations and jobs in place.
Since opening Canadian operations in 2020, the company has grown to a p… [+1999 chars]
An opinionated perspective on how to do important research that makes a difference (and sometimes win awards).
At EuroCrypt last week
month
year[a]Yes, it did take me eight months to write this blog post. I am slow at writing.
I was honored to receive a best paper award
for a model stealing paper I wrote… [+56394 chars]
This is a little embarrassing to share, but I’d rather someone else be able to spot a dangerous scam before they fall for it. So, here goes. One evening last month, my Apple Watch, iPhone, and Mac all lit up with a message prompting me to reset my password. T…
This is a little embarrassing to share, but I’d rather someone else be able to spot a dangerous scam before they fall for it. So, here goes.
One evening last month, my Apple Watch, iPhone, and Mac a… [+2633 chars]
Over the past decade, payment systems have undergone a dramatic transformation. The advent of mobile technology has not only introduced new digital
Over the past decade, payment systems have undergone a dramatic transformation. The advent of mobile technology has not only introduced new digital wallets and biometric authentication but has also p… [+8267 chars]
Pro-American lobby groups cautiously praised President Donald Trump's decision to pick Sen. Markwayne Mullin as the new Secretary of the Department of Homeland Security.
The post Pro-American Groups Welcome Trump’s DHS Pick Markwayne Mullin appeared first on …
Pro-American lobby groups cautiously praised President Donald Trump’s decision to pick Sen. Markwayne Mullin as the new Secretary of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS).
“We’re congratulating … [+20762 chars]
Hello Everyone Glad to Join the Community - posted in Introductions: Hi everyone,
I recently came across BleepingComputer while researching some tech topics and decided to join the community. I’m interested in learning more about computer security, software…
Hi everyone,
I recently came across BleepingComputer while researching some tech topics and decided to join the community. I’m interested in learning more about computer security, software, and trou… [+130 chars]
The newly launched Hiroh Phone enters the market with a specialized focus on anti-surveillance, targeting users such as journalists, activists, and security professionals. Unlike standard smartphones that rely on software permissions to manage sensor access, …
The newly launched Hiroh Phone enters the market with a specialized focus on anti-surveillance, targeting users such as journalists, activists, and security professionals. Unlike standard smartphones… [+2620 chars]
SEBI launches voluntary folio lock for mutual fund investors, allowing debit freeze on demat and non-demat folios from April 30 to boost portfolio security.
In a bid to promote the digital security of units of investors in Mutual Funds, the capital market regulator SEBI has introduced a voluntary debit freeze facility across demat and non-demat folios.
… [+769 chars]
Myanmar’s military regime has announced the implementation of the Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR), a system designed to track mobile devices across cellular networks, prompting concerns from technical experts that it could be used to monitor citize…
Myanmars military regime has announced the implementation of the Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR), a system designed to track mobile devices across cellular networks, prompting concerns fro… [+2891 chars]
CNN:
FBI investigating ‘suspicious’ cyber activities on critical surveillance network — Federal agencies Digital security National security — The FBI has identified a suspected cybersecurity incident on a sensitive network used to manage wiretaps and inte…
memeorandum is an auto-generated summary of the stories that US political commentators are discussing online right now.
Unlike sister sites Techmeme and Mediagazer, it is not a human-edited news out… [+72 chars]
A GlobalData poll highlights cyber insurance growth expectations as the Middle East conflict heightens geopolitical and digital risk concerns.
Tensions surrounding the escalating conflict involving the US, Israel, and Iran have begun to ripple through global insurance markets, with insurers rapidly reassessing risk exposures linked to shipp… [+3306 chars]
Following major data leaks at Odido and health services, a motion tabled by the Dutch opposition argues that online safety shouldn't depend on your income and calls on the government to hand every citizen a free "digital first-aid kit."
<ul><li>Dutch MPs are asking for a free "basic digital security package" for citizens</li><li>Some recent major national data leaks triggered the motion</li><li>The suite should include VPN, ad block… [+3308 chars]
The Air 4 Pro Limited Justice Edition smart glasses I tested at MWC 2026 put a 201-inch virtual Micro-OLED in front of my eyes, letting me live out my superhero dreams.
BARCELONA—My first stop here at MWC took me on a virtual trip to Gotham City. TCL's RayNeo…
My Experience
I'm PCMag's managing editor for consumer electronics, overseeing an experienced team of analysts covering smart home, home entertainment, wearables, fitness and health tech, and variou… [+2290 chars]