
From PQC Assessment to AI Recommendations: Preparing for the Post-Quantum World
Quantum computing is no longer a distant concept. As it moves from theory to real-world application, it introduces a new set of security risks for digital systems. The cryptographic algorithms that currently protect financial transactions, communications, and data exchanges may not be strong enough to withstand quantum-based attacks. Assessing Post-Quantum (PQ) security has become a critical step in preparing organizations for this transition. When combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI), PQ security assessment provides a structured, data-driven approach to evaluate risks, identify vulnerabilities, and guide secure migration strategies. This article explores how Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and AI work together to help organizations strengthen and future-proof their cryptographic infrastructure.
1. Understanding PQ Assessment
Post-Quantum risk assessment evaluates how vulnerable an organization’s cryptographic systems are to quantum-based attacks. The process begins by mapping all cryptographic assets, including algorithms, protocols, and key management systems, and identifying where traditional cryptography such as RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) or ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) is still in use. The assessment measures exposure, estimates potential impact, and classifies risk levels. It also examines dependencies such as hardware acceleration, interoperability with legacy systems, and regulatory requirements. The result is a clear understanding of the organization’s quantum readiness. This serves as a baseline for prioritizing which components should transition first and how to plan the migration with minimal disruption.
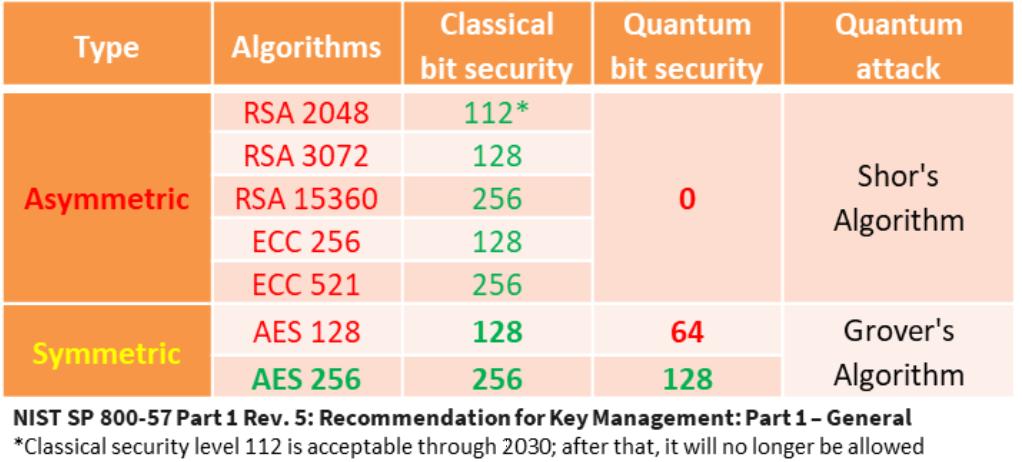
2. AI in the PQ Landscape
AI will increasingly contribute to making PQ assessments more efficient and actionable. Traditional assessments rely heavily on manual review and static analysis, but AI can automate much of this process.
Machine learning models can:
-
Detect cryptographic assets across large and complex systems.
-
Classify algorithms and identify quantum-vulnerable implementations based on NIST and other relevant standards.
-
Assess risk levels based on exposure patterns and usage frequency.
-
Evaluate the impact of adopting different PQ KEM and Signature algorithms on system performance and interoperability.
-
Recommend appropriate PQ migration strategies to enhance resistance against quantum attacks.
AI not only speeds up the assessment process but also improves precision. By learning from historical data and continuous evaluations, AI systems refine their recommendations over time, providing more accurate and context-aware insights.
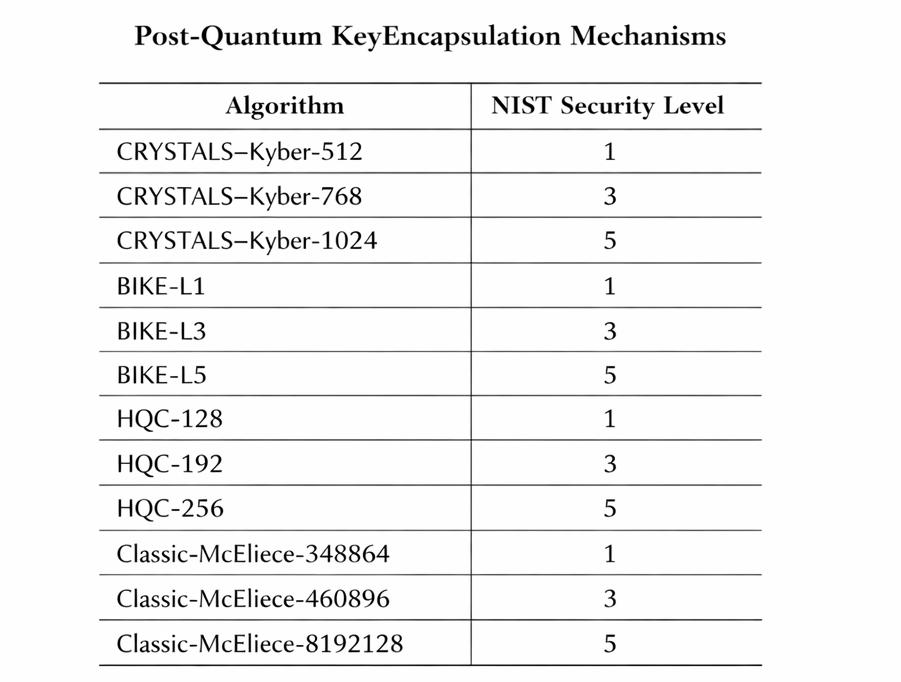
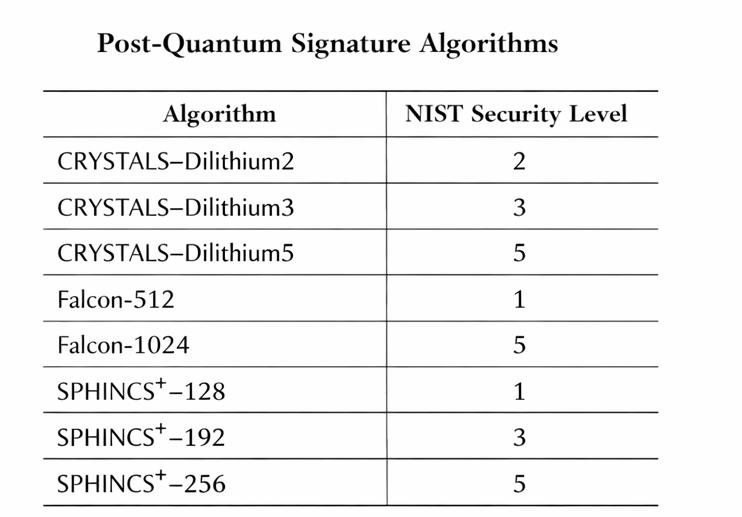
3. From Assessment to Action: AI-Driven Recommendations
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is planning migration. AI-driven recommendations are essential in this phase.
AI tools can compare candidate PQ algorithms based on:
-
Security strength and maturity.
-
Compatibility with existing systems.
-
Performance metrics such as speed, bandwidth, and energy efficiency.
-
Compliance with evolving standards, including NIST’s PQC guidelines.
Using these factors, AI can generate tailored migration roadmaps that rank algorithms by suitability and guide step-by-step implementation. This enables organizations to transition toward quantum-safe solutions with confidence and reduced risk.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is redefining how we approach digital security, bringing both new challenges and opportunities. Organizations starting their post-quantum journey today will be better positioned to protect critical data and maintain trust and resilience as the digital landscape evolves. By combining AI-driven PQ assessments with a crypto-agile approach, companies can identify risks faster, select the most suitable quantum-safe algorithms, and adapt migration strategies as threats and standards evolve. Ultimately, the future of cryptography depends on being both PQ-ready and crypto-agile, ensuring systems remain resilient and adaptable in the post-quantum era.
Edited By: Windhya Rankothge, PhD, Canadian Institute for Cybersecurity
References
-
Ivezic, M. (2024). Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) meets Quantum AI (QAI). PostQuantum. https://postquantum.com/post-quantum/pqc-quantum-ai-qai/
-
Sanzeri, S. (2024). The impact of AI on post-quantum cybersecurity. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/02/06/the-impact-of-ai-on-post-quantum-cybersecurity/
-
Mosca, M. (2018). Cybersecurity in an era with quantum computers: Will we be ready? IEEE Security & Privacy, 16(5), 38–41. IEEE. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8490169
-
Kong, I., Janssen, M., & Bharosa, N. (2024). Realizing quantum-safe information sharing: Implementation and adoption challenges and policy recommendations for quantum-safe transitions. Government Information Quarterly, 41(1), 101884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2023.101884
-
Sadeghi, S., Chouhan, V., Aldarwbi, M., Ghorbani, A., Chow, A., & Burko, R. (2025). Securing financial sector applications in the quantum era: A comprehensive evaluation of NIST’s recommended algorithms through use-case analysis. Expert Systems with Applications, 128243. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2025.128243
-
Barker, E. (2020). Recommendation for key management: Part 1 (Revised)(May 2020 edition) – General. NIST Special Publication, 800. https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-57-part-1/rev-5/final
-
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2025, September). Mappings of migration to PQC project capabilities to risk framework documents (NIST CSWP 48, Initial Public Draft). https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.48.ipd.pdf
-
evolutionQ Inc., & Global Risk Institute. (2024). Quantum threat timeline report 2024. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: evolutionQ Inc. under license by Global Risk Institute. https://www.globalriskinstitute.org/publication/2024-quantum-threat-timeline-report/
-
National Security Agency. (2025). Announcing the Commercial National Security Algorithm Suite 2.0 [Tech. guidance memo]. https://media.defense.gov/2025/May/30/2003728741/-1/-1/0/CSA_CNSA_2.0_ALGORITHMS.PDF
-
Australian Signals Directorate. (2025). Cryptographic roadmap – Preparing for post-quantum cryptography (Version 1.0). https://www.cyber.gov.au/resources-business-and-government/essential-cybersecurity/ism/cybersecurity-guidelines/guidelines-cryptography